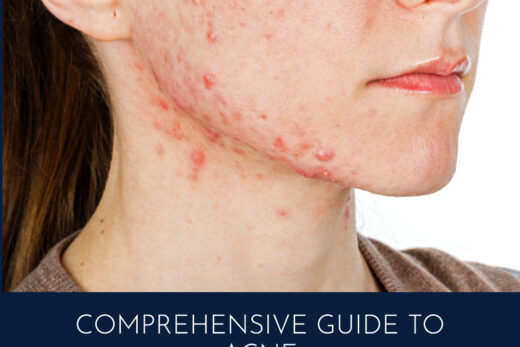
Hormonal acne is a widespread skin issue with deep roots in our hormonal makeup. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll unpack the causes, discuss various management strategies, and delve into prevention methods for this condition. Our goal is to provide clear, practical insights into navigating hormonal acne effectively. Let’s dive straight into this vital topic.
Understanding Hormonal Acne
Hormonal acne, characterized by the formation of pimples due to hormonal fluctuations, commonly affects teenagers and adults undergoing hormonal changes. It is particularly prevalent in women during menstrual cycles, pregnancy, or menopause.
The Role of Hormones in Acne
Hormones play a crucial role in the development and severity of acne. Here are the key players:
Androgens
Estrogens
Cortisol
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1)
Progesterone
Key Takeaways #1
In the hormonal interplay affecting acne, estrogens stand out as the only hormones known to reduce sebum production, aiding in acne prevention. In contrast, other hormones like androgens, cortisol, IGF-1, and progesterone can escalate sebum production, often exacerbating acne. It’s crucial to note that falling estrogen levels could heighten acne risk, underscoring the hormone’s protective role against acne.
Causes of Hormonal Acne
Hormonal acne is caused by several factors:
Hormonal Imbalance
Oral Contraceptives
High Glycemic Diet
Stress
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Puberty
Key Takeaways #2
Hormonal acne emerges from a confluence of factors, most significantly hormonal imbalances, such as elevated androgen levels or falling estrogen levels, causing excessive sebum production. Other triggers include certain oral contraceptives, high glycemic diets, stress, and conditions like PCOS, all promoting androgen production or reducing estrogen’s protective effect. Thus, maintaining estrogen levels could be a key strategy to counteract hormonal acne.
Diagnosis and Tests for Hormonal Acne
Diagnosing hormonal acne involves looking at various factors:
Clinical Examination
Hormonal Testing
Medical History
Skin and Hair Analysis
Key Takeaways #3
Diagnosing hormonal acne requires a multi-pronged approach involving clinical examination, hormonal testing, and an in-depth review of medical history. Identifying the signs of hormonal imbalance on the skin and hair can provide additional clues. Understanding the interplay of these factors is pivotal in crafting an effective management plan for hormonal acne.
Management and Treatment of Hormonal Acne
Managing hormonal acne involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatments:
Dietary Changes (Regulates insulin and IGF-1)
Stress Management (Lowers cortisol)
Oral Contraceptives (Regulates estrogen, progesterone, and androgens)
Spironolactone (Reduces androgens)
Topical Retinoids
Probiotics
Key Takeaways #4
The management of hormonal acne revolves around a balanced diet, stress management, and medications such as oral contraceptives, spironolactone, and topical retinoids. Probiotics have also shown promise in mitigating acne. However, these strategies should be pursued under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure safety and efficacy.
Other Treatments for Hormonal Acne
Additional medical interventions may be needed in some cases:
Isotretinoin
Hormone Therapy
Chemical Peels
Laser and Light Therapy
Key Takeaways #5
In severe cases, additional interventions like isotretinoin, hormone therapy, chemical peels, and laser/light therapy might be required. These procedures can offer relief from persistent acne but should only be initiated following a thorough discussion with a healthcare professional, given their potential side effects and the individualized nature of acne treatment.
Prevention of Hormonal Acne
Here are some tips to prevent hormonal acne:
Maintain a Healthy Diet
Manage Stress
Regular Skin Care Routine
Probiotic-rich Foods
Key Takeaways #6
Tips to prevent hormonal acne:
- Balanced diet low in refined sugars and carbs to regulate hormones.
- Effective stress management techniques to control cortisol levels.
- Regular skincare routins with non-comedogenic products to prevent pore blockage.
- Consuming probiotic-rich foods can potentially reduce inflammation.
Impact of Hormonal Acne on Skin Health
Hormonal acne can significantly impact skin health:
Skin Texture and Appearance
Psychological and Emotional Impact
Importance of Skincare Routines
Key Takeaways #7
- Hormonal acne can profoundly impact skin health, causing inflammation, redness, swelling, and scarring.
- The psychological toll of hormonal acne can lead to stress and anxiety, affecting overall wellbeing.
- Maintaining regular and appropriate skincare routines are essential in managing hormonal acne and promoting skin health.
Duration and Expectations of Hormonal Acne
The duration and severity of hormonal acne can vary:
Typical Duration of Breakouts
Factors Affecting Duration
Timeline for Improvement
Key Takeaways #8
- Hormonal acne’s duration and severity can vary based on individual hormonal fluctuations and the promptness of treatment.
- Factors such as stress, diet, menstrual cycle, and hormonal imbalances can influence the duration of hormonal acne.
- With proper treatment, most individuals see improvement in their hormonal acne within three to four months.
Differentiating Hormonal Acne from Bacterial Acne
Here’s how to tell the difference between hormonal and bacterial acne:
Location of Acne
Appearance of Acne
Underlying Cause
You can learn more about acne types here
Key Takeaways #9
Hormonal and bacterial acne, while both forms of acne, can be distinguished by their location, appearance, and underlying causes. Hormonal acne, often characterized by deep, painful cysts or nodules, typically appears in hormone-sensitive areas like the lower face, jawline, and neck, and is driven by hormonal fluctuations. On the other hand, bacterial acne can occur anywhere on the face, especially the T-zone, and presents a mix of whiteheads, blackheads, papules, and pustules. It arises due to an overgrowth of the bacteria P. acnes within the skin’s pores. Understanding these differences can help guide appropriate treatment strategies.
Natural Approaches to Balancing Hormones
Here are some natural ways to help balance hormones and potentially reduce acne:
Exercise
Sleep
Stress Management
Healthy Diet
Key Takeaways #10
Hormonal and bacterial acne, while both forms of acne, can be distinguished by their location, appearance, and underlying causes. Hormonal acne, often characterized by deep, painful cysts or nodules, typically appears in hormone-sensitive areas like the lower face, jawline, and neck, and is driven by hormonal fluctuations. On the other hand, bacterial acne can occur anywhere on the face, especially the T-zone, and presents a mix of whiteheads, blackheads, papules, and pustules. It arises due to an overgrowth of the bacteria P. acnes within the skin’s pores. Understanding these differences can help guide appropriate treatment strategies.
Conclusion
To wrap things up, hormonal acne is a skin condition deeply rooted in the subtle dance of our hormones. It’s influenced by a myriad of factors including our diet, stress levels, and individual health conditions. Tackling it requires a harmonious blend of balanced lifestyle choices, a dedicated skincare regimen, and at times, professional medical intervention. The path to managing hormonal acne may seem winding, but with a keen understanding of your body’s unique hormonal dynamics and potential triggers, the journey becomes less daunting. Remember, every step you take is a step towards healthier skin and a more confident you.